Unravelling the Inner Workings: Essential Parts in an Electrical Generator
In the realm of electrical engineering, generators hold a prominent position as the backbone of power generation systems. These marvelous machines harness mechanical energy and convert it into electrical power, fueling industries, homes, and communities worldwide. At the core of every electrical generator lies a symphony of essential parts, each playing a crucial role in ensuring a seamless flow of electricity. In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of these indispensable components that breathe life into the world of electricity generation.
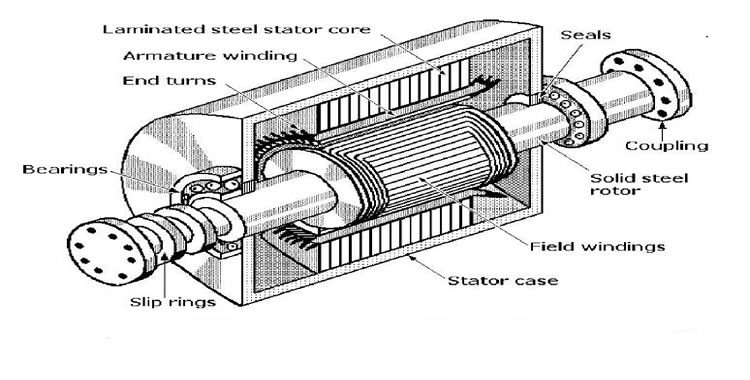
Rotor and Stator
At the heart of an electrical generator lies the dynamic duo of the rotor and stator. The rotor, mounted on the shaft, serves as the rotating component, while the stator remains stationary, enveloping the rotor. Together, they form the magnetic field essential for electromagnetic induction, a fundamental principle that drives the generation process.
Exciter
The exciter, a smaller generator within the generator, serves as the key to initiating and maintaining the magnetic field. By providing a small direct current (DC) voltage to the rotor’s field windings, it sets the stage for generating electricity on a grand scale.
Field Windings
The field windings are coils of wire wrapped around the rotor, responsible for generating the magnetic field when supplied with electric current. The strength and stability of the magnetic field depend on the excitation level, affecting the generator’s performance.
Armature Windings
On the stator resides the armature windings, an intricate network of copper coils. As the magnetic field from the rotor interacts with these windings, the process of electromagnetic induction begins, generating alternating current (AC) voltage across the output terminals.
Prime Mover
The prime mover, the powerhouse of the generator, provides the necessary mechanical energy to turn the rotor. Common prime movers include gas turbines, steam turbines, and internal combustion engines, each playing a pivotal role in driving the generator’s operation.
Bearings
Efficient and smooth rotation is paramount in a generator’s functioning, and that’s where bearings come into play. They minimize friction and allow the rotor to spin freely, reducing wear and tear on the components and ensuring longevity.
Governor
Stability is the key to consistent power generation, and the governor takes charge of this critical task. By regulating the prime mover’s speed, it ensures that the generator maintains a constant frequency, a vital aspect of a reliable power supply.
Cooling System
Electrical generators generate substantial heat during operation, necessitating an effective cooling system. Fans or water-based cooling mechanisms keep the temperature in check, preventing overheating and maintaining peak efficiency.
Voltage Regulator
To maintain a steady output voltage despite varying loads, the voltage regulator steps up or steps down the generated voltage as required. This vital component ensures that the electricity flowing out of the generator remains stable and safe for consumption.
The Wrap Up
In conclusion, electrical generators are a marvel of engineering ingenuity, with their useful parts working in harmony to produce the lifeblood of our modern society – electricity. From the dynamic rotor-stator duo to the precise voltage regulator, each component plays a crucial role in the smooth functioning of these powerhouses. Understanding the inner workings of generators not only deepens our appreciation for the technology but also highlights the constant efforts of electrical engineers to refine and enhance these essential machines. So, the next time you flick a light switch or power up your devices, take a moment to acknowledge the incredible orchestration of parts that make it all possible.

